Boils Treatment & Prevention Strategies for Healthy Skin
867
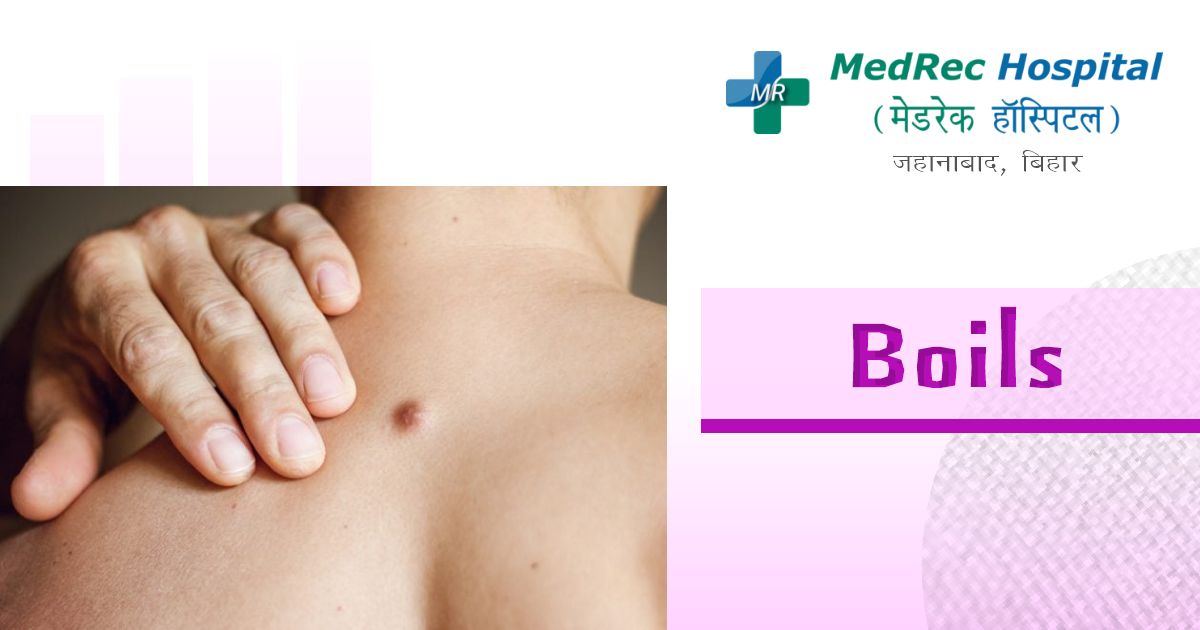
When bacteria invade and irritate one or more of your hair follicles, a painful, pus-filled swelling under your skin known as a boil develops. A carbuncle is a group of boils that come together to form an infectious area under the skin.
Typically, boils (furuncles) begin as sensitive, reddish or purple lumps. Before they rupture and discharge, the lumps quickly fill with pus, enlarging and becoming more painful. The face, back of the neck, armpits, thighs, and buttocks are the regions most prone to be impacted.
Usually, a single boil may be cured at home. However, avoid trying to puncture or squeeze it because doing so might spread the illness.
Causes Of Boils
Staphylococcus aureus, a species of bacteria frequently found on the skin and inside the nose, is the main cause of boils. A lump forms when pus amasses below the skin. On occasion, boils develop where the skin has been pierced by a small cut or an insect bite, enabling the bacteria free access.
How to check if you have Boils?
A single, minor boil may often be treated by you on your own. Please seek medical advice, if you have more than one boil at once or if a boil:
- On your face or has an impact on your vision
- Quickly worsening
- Gives excruciating pain
- Brings on a fever
- Despite self-care, becomes larger
- Not recovered after two weeks
- Reoccurs
Boils Risk Factors
Anyone can get boils or carbuncles, even generally healthy people, however the following things might make you more likely to do so:
Close association with a staph-infected individual. If you share a residence with someone who has a boil or carbuncle, your chances of getting an infection increase.
Diabetes. Your body's ability to fight infection, especially bacterial skin infections, may be hampered by this illness.
Different skin problems. Boils and carbuncles are more likely to affect you if you have skin issues like acne and eczema because they harm your skin's protective barrier.
Weakened immunity. You are more prone to boils and carbuncles if your immune system is compromised for any cause.
Symptoms Of Boils
Boils
Boils can arise anywhere on your body, but they are more common in hair-bearing regions like the face, back of the neck, armpits, thighs, and buttocks where you are most likely to perspire or come into contact with anything. Typical indications and symptoms of a boil include:
- A tiny, painful, red lump that can grow to be more than 2 inches in diameter (5 centimeters)
- Swelling, reddish or purple skin around the lump
- The lump getting bigger over a few days as it swells with pus
- The formation of a yellow-white point that finally bursts, allowing the pus to flow out
Carbuncles
A group of boils that are joined and produce an infection are called carbuncles. When compared to a single boil, a carbuncle produces a more intense and painful rash.
Prevention From Boils
Boils can occasionally be difficult to avoid, especially if your immune system is compromised. The following steps could assist you in preventing staph infections:
Regularly wash your hands with a light soap. Or often apply hand lubricant with alcohol. Your best line of defence against pathogens is careful hand washing.
Maintain wound cover. Till they heal, keep wounds and abrasions clean and bandaged with sterile, dry gauze.
Do not exchange personal goods like towels, bedding, razors, clothes, and sporting gear. Infections with Staph can spread from person to person as well as via objects. Wash your towels and linens with detergent and hot water with bleach added if you have a cut or sore, and then dry them in a hot dryer.
Treatments
Small boils may often be treated at home by applying warm compresses to reduce discomfort and encourage natural drainage.
Treatment options for bigger boils and carbuncles may include:
Drainage and incision. Your doctor may make an incision in a large boil or carbuncle to drain it. Sterile gauze may be used to pack deep infections that can not be fully drained in order to help soak up and drain more pus.
Antibiotics. Antibiotics might occasionally be recommended by your doctor to treat serious or recurrent illnesses.
In situations of small boils, the following actions may speed up the healing process and prevent the illness from spreading:
Hot compresses. Use a warm washcloth or compress on the afflicted region for about 10 minutes each time throughout the day. The outcome is that the boil will rupture and drain more quickly.
Never manually puncture or squeeze a boil. The infection may spread as a result.
Keep contamination at bay. After you have treated a boil, properly wash your hands. Additionally, especially if you have recurring infections, wash any clothes, towels, or compresses that have come into contact with the diseased region.
Complications of Boils
Please contact your doctor if you face any of the following:
- Your face is covered with a boil.
- You have a boil and a chronic illness like diabetes.
- Your boil's surrounding skin is hot and uncomfortable.
- You have had a boil for two weeks, yet nothing you have done has worked.
- You continue to have boils
- You have many boils (carbuncle)
- You feel feverish and shivery, and you have a boil.
For further information please access the following resources:
Emergency : +91 89686 77907
Front Desk : +91 98018 79584
Page last reviewed: Mar 14, 2023
Next review due: Mar 14, 2025






.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)